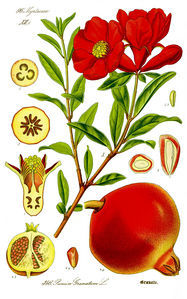
Punica granatum
Punica granatum L.
| Ordre | Myrtales |
|---|---|
| Famille | Lythraceae |
| Genre | Punica |
2n = 16, 18
Origine : Asie centrale, Inde
sauvage ou cultivé
| Français | grenadier |
|---|---|
| Anglais | pomegranate |
- fruit comestible (formes douces)
- formes acides du fruit : ingrédient culinaire, frais ou concentré
- écorce du fruit et des racines : tanin et colorant
- fleurs : médicinale
- forme du fruit source d'inspiration artistique
The traditional area of cultivation reaches from the Himalaya to the Mediterranean area. Now cultivated in most countries with warmer climate, also escaped from cultivation and naturalized (e.g. in N Albania). Very old fruit tree, already in the early Bronze age known from the Middle East. Punica protopunica Balf.f. (in Proc. Roy. Soc. Edinbg. 9, 1882, 512) from Socotra had been discussed as a possible progenitor, but this is rather doubtful. A multiple domestication within the large area of the wild P. granatum is now generally accepted. The fruits are consumed fresh. The pulpa of the seeds is eaten or prepared into a juice, which is the basis for lemonades or a beverage similar to wine. In India the dried and ground seeds are used as a condiment (anardana). Medicinally used are flowers (Flores balaustinorum, Flores Granati, Flores Balaustia) and the fruit peel which is rich in tannin (Cortex fructus Granati, Cortex malicorii, Malicorium, Pericarpium Granati), also used for tanning as the root bark (Cortex Radicis Granati). From the flowers a red dye is extracted. Also ornamental plant with simple and double flowers.
Sommaire
Description
Noms populaires
| français | grenadier / grenade |
| anglais | pomegranate |
| allemand | Granatapfelbaum / Granatapfel |
| néerlandais | granaatappel |
| italien | melograno ; melogranato / melagrana ; mela granata |
| espagnol | granado / granada |
| catalan | magraner / magrana, mangrana |
| portugais | romãzeira ; romanzeira (Brésil) / romã |
| arabe | rummān |
| grec ancien | ῥόα, ῥοιά - rhoa, rhoia (Théophraste), ῥόα - rhoa (Dioscoride) |
- Voir les noms dans toutes les langues européennes
- Voir les noms de la Flore populaire d'Eugène Rolland
Classification
Punica granatum L. (1753)
synonyme : Punica nana L. (1762)
Cultivars
- Gallesio, 1817-1839, Pomona Italiana
Histoire
Usages
- Voir Edible plants de Sturtevant (1919)
- Voir l'Origine des plantes cultivées de Candolle (1882)
- Voir les Plantes médicinales de Cazin (1868)
{{{texte}}}
The traditional area of cultivation reaches from the Himalaya to the Mediterranean area. Now cultivated in most countries with warmer climate, also escaped from cultivation and naturalized (e.g. in N Albania). Very old fruit tree, already in the early Bronze age known from the Middle East. Punica protopunica Balf.f. (in Proc. Roy. Soc. Edinbg. 9, 1882, 512) from Socotra had been discussed as a possible progenitor, but this is rather doubtful. A multiple domestication within the large area of the wild P. granatum is now generally accepted. The fruits are consumed fresh. The pulpa of the seeds is eaten or prepared into a juice, which is the basis for lemonades or a beverage similar to wine. In India the dried and ground seeds are used as a condiment (anardana). Medicinally used are flowers (Flores balaustinorum, Flores Granati, Flores Balaustia) and the fruit peel which is rich in tannin (Cortex fructus Granati, Cortex malicorii, Malicorium, Pericarpium Granati), also used for tanning as the root bark (Cortex Radicis Granati). From the flowers a red dye is extracted. Also ornamental plant with simple and double flowers.
Propriétés
- Voir la composition nutritionnelle de la grenade fraîche du CIQUAL (ANSES, France)
- Voir la composition nutritionnelle de la grenade fraîche du National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference (USDA)
Rôle dans les cultures humaines
Références
- Agrimaroc, 2004. Le grenadier. télécharger le pdf
- Chauvet, Michel, 2018. Encyclopédie des plantes alimentaires. Paris, Belin. 880 p. (p. 425)
- Evreinoff V.A., 1957. Contribution à l'étude du grenadier. J. Agric. Trop. Bot. Appl., 4 : 124-138.
- Goor, Asaph, 1967. The history of the pomegranate in the Holy Land. Econ. Bot., 21 : 215-229.
- Holland, D., Hatib, K. & Bar-Ya’akov, I. Pomegranate: Botany, Horticulture, Breeding. Section of Deciduous Fruit Trees Sciences, Newe Ya’ar Research Center, Agricultural Research Organization, Israel. télécharger le pdf
- Janick, Jules & Paull, Robert E., 2008. The Encyclopedia of Fruit and Nuts. Cambridge (USA), CABI. 954 p.
- Lüdders P. & Debor H.W., 1978. Bibliographie des internationalen Granatapfel-Schrifttums. Aktuelle Literaturinformationen aus dem Obstbau (Technische Univ., Berlin), n° 73.
- Mars, Messaoud & Marrakchi, Mohamed M., 1999. Diversity of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) germplasm in Tunisia. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 46: 461-467.
- Mars, Messaoud, 2000. Pomegranate plant material: Genetic resources and breeding, a review. in : Melgarejo P. (ed.), Martínez-Nicolás J.J. (ed.), Martínez-Tomé J. (ed.). Production, processing and marketing of pomegranate in the Mediterranean region: Advances in research and technology. Options Méditerranéennes, Série A. Séminaires Méditerranéens: n. 42). pp. 55-62. en ligne au CIHEAM.
- Mars, Messaoud, 2001. Le grenadier (Punica granatum L.). Thèse Montpellier.
- Morton, Julia F., 1987. Fruits of warm climates. Miami. Pomegranate : pp. 352–355. en ligne à New Crop Purdue.
- Mure, Véronique, 2013. Le grenadier et la balustre… Botanique, Jardins, Paysages.
- Popenoe, Wilson, 1974. Manual of tropical and subtropical fruits. Excluding the banana, coconut, pineapple, citrus frits and fig. Ed. 1 : 1920, Macmillan Company. Reprint 1974, Hafner. Grenadier : pp 375-383.
- Rollet, Bernard et coll., 2010. Arbres des Petites Antilles. Tome 1 : Introduction à la dendrologie. 276 p. Tome 2 : Description des espèces. 866 p. + 46 pl. coul. + CD de photos sur l'anatomie du bois. Basse-Terre, ONF. Voir sur Pl@ntUse.
- Seeram, Navindra P., Schulman, Risa N. & Heber, David, 2006. Pomegranates: Ancient Roots to Modern Medicine. CRC Press. (Medicinal and Aromatic Plants – Industrial Profiles).
Liens
- BHL
- California Rare Fruits Growers
- Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases
- Encyclopedia of Life
- FAO Ecocrop
- Flora of China
- Flora of Pakistan
- Grieve's herbal
- GRIN
- IPNI
- Mansfeld
- Moerman, Native American Ethnobotany
- Multilingual Plant Name Database
- NewCrop Purdue
- Plant List
- Plants for a future
- Pommiers.com
- PROSEA sur Pl@ntUse
- PROTA sur Pl@ntUse
- Pomegranate tree: description and use (projet européen RESGEN29 "Conservation, evaluation, exploitation and collection of minor fruit tree species")
- TAXREF
- Tela Botanica
- Wikipédia
- Wikiphyto
- World Agroforestree