Punica granatum : Différence entre versions
De PlantUse Français
| Ligne 6 : | Ligne 6 : | ||
|famille = Lythraceae | |famille = Lythraceae | ||
|genre = Punica | |genre = Punica | ||
| − | |nb chromosomes = 2n = 16 | + | |nb chromosomes = 2n = 16, 18 |
|origine = Asie centrale, Inde | |origine = Asie centrale, Inde | ||
|statut = sauvage ou cultivé | |statut = sauvage ou cultivé | ||
|français = '''grenadier''' | |français = '''grenadier''' | ||
|anglais = '''pomegranate''' | |anglais = '''pomegranate''' | ||
| + | }}{{Encadré | ||
| + | |color=lightgreen | ||
| + | |titre=Résumé des usages | ||
| + | |texte=*fruit comestible (formes douces) | ||
| + | *formes acides du fruit : ingédient culinaire, frais ou concentré) | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| Ligne 28 : | Ligne 32 : | ||
== Noms populaires == | == Noms populaires == | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:100%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:100%;" | ||
| − | + | | français | |
| − | + | | grenadier / grenade | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | | anglais | |
| + | | pomegranate | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | allemand | ||
| + | | Granatapfelbaum / Granatapfel | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | néerlandais | ||
| + | | granaatappel | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | italien | ||
| + | | melograno ; melogranato / melagrana ; mela granata | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | espagnol | ||
| + | | granado / granada | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | catalan | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | portugais | ||
| + | | romãzeira ; romanzeira (Brésil) / romã | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | arabe | ||
| + | | rummān | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | grec ancien | ||
| + | | ῥόα, ῥοιά - rhoa, rhoia [[Noms grecs de Théophraste#rhoa|(Théophraste)]], ῥόα - rhoa [[rhoa (Dioscoride)|(Dioscoride)]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | *Voir les noms dans toutes les [[:en:Punica granatum (Common names)|langues européennes]] | ||
| + | *Voir les noms de la [[Punica (Rolland, Flore populaire)|''Flore populaire'' d'Eugène Rolland]] | ||
== Classification == | == Classification == | ||
| Ligne 88 : | Ligne 115 : | ||
== Références == | == Références == | ||
*Agrimaroc, 2004. Le grenadier. [http://www.agrimaroc.net/123.pdf télécharger le pdf] | *Agrimaroc, 2004. Le grenadier. [http://www.agrimaroc.net/123.pdf télécharger le pdf] | ||
| + | *Chauvet, Michel, 2018. ''[[Encyclopédie des plantes alimentaires]]''. Paris, Belin. 880 p. (p. 425) | ||
*Evreinoff V.A., 1957. Contribution à l'étude du grenadier. ''J. Agric. Trop. Bot. Appl.'', 4 : 124-138. | *Evreinoff V.A., 1957. Contribution à l'étude du grenadier. ''J. Agric. Trop. Bot. Appl.'', 4 : 124-138. | ||
*Goor, Asaph, 1967. The history of the pomegranate in the Holy Land. ''Econ. Bot.'', 21 : 215-229. | *Goor, Asaph, 1967. The history of the pomegranate in the Holy Land. ''Econ. Bot.'', 21 : 215-229. | ||
| Ligne 119 : | Ligne 147 : | ||
*[http://www.pommiers.com/grenadier/grenade.htm Pommiers.com] | *[http://www.pommiers.com/grenadier/grenade.htm Pommiers.com] | ||
*[[:en:Punica granatum (PROSEA)|PROSEA sur Pl@ntUse]] | *[[:en:Punica granatum (PROSEA)|PROSEA sur Pl@ntUse]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
*[[Punica granatum (PROTA)|PROTA sur Pl@ntUse]] | *[[Punica granatum (PROTA)|PROTA sur Pl@ntUse]] | ||
*[http://www.ueresgen29.unifi.it/ds2.htm Pomegranate tree: description and use] (projet européen [http://www.ueresgen29.unifi.it/ RESGEN29 "Conservation, evaluation, exploitation and collection of minor fruit tree species"]) | *[http://www.ueresgen29.unifi.it/ds2.htm Pomegranate tree: description and use] (projet européen [http://www.ueresgen29.unifi.it/ RESGEN29 "Conservation, evaluation, exploitation and collection of minor fruit tree species"]) | ||
Version du 22 novembre 2019 à 19:27
Punica granatum L.
| Ordre | Myrtales |
|---|---|
| Famille | Lythraceae |
| Genre | Punica |
2n = 16, 18
Origine : Asie centrale, Inde
sauvage ou cultivé
| Français | grenadier |
|---|---|
| Anglais | pomegranate |
Résumé des usages
- fruit comestible (formes douces)
- formes acides du fruit : ingédient culinaire, frais ou concentré)
Sommaire
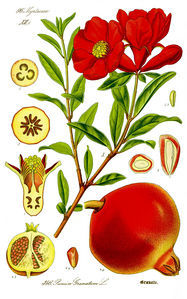
Description
Noms populaires
| français | grenadier / grenade |
| anglais | pomegranate |
| allemand | Granatapfelbaum / Granatapfel |
| néerlandais | granaatappel |
| italien | melograno ; melogranato / melagrana ; mela granata |
| espagnol | granado / granada |
| catalan | |
| portugais | romãzeira ; romanzeira (Brésil) / romã |
| arabe | rummān |
| grec ancien | ῥόα, ῥοιά - rhoa, rhoia (Théophraste), ῥόα - rhoa (Dioscoride) |
- Voir les noms dans toutes les langues européennes
- Voir les noms de la Flore populaire d'Eugène Rolland
Classification
Punica granatum L. (1753)
synonyme : Punica nana L. (1762)
Cultivars
Histoire
Usages
- Voir Edible plants de Sturtevant (1919)
- Voir l'Origine des plantes cultivées de Candolle (1882)
- Voir les Plantes médicinales de Cazin (1868)
- Voir Edouard Le Floc'h, Contribution à une étude ethnobotanique de la flore tunisienne, 1983.
Propriétés
- Voir la composition nutritionnelle de la grenade fraîche du CIQUAL (ANSES, France)
- Voir la composition nutritionnelle de la grenade fraîche du National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference (USDA)
Rôle dans les cultures humaines
Références
- Agrimaroc, 2004. Le grenadier. télécharger le pdf
- Chauvet, Michel, 2018. Encyclopédie des plantes alimentaires. Paris, Belin. 880 p. (p. 425)
- Evreinoff V.A., 1957. Contribution à l'étude du grenadier. J. Agric. Trop. Bot. Appl., 4 : 124-138.
- Goor, Asaph, 1967. The history of the pomegranate in the Holy Land. Econ. Bot., 21 : 215-229.
- Holland, D., Hatib, K. & Bar-Ya’akov, I. Pomegranate: Botany, Horticulture, Breeding. Section of Deciduous Fruit Trees Sciences, Newe Ya’ar Research Center, Agricultural Research Organization, Israel. télécharger le pdf
- Janick, Jules & Paull, Robert E., 2008. The Encyclopedia of Fruit and Nuts. Cambridge (USA), CABI. 954 p.
- Lüdders P. & Debor H.W., 1978. Bibliographie des internationalen Granatapfel-Schrifttums. Aktuelle Literaturinformationen aus dem Obstbau (Technische Univ., Berlin), n° 73.
- Mars, Messaoud & Marrakchi, Mohamed M., 1999. Diversity of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) germplasm in Tunisia. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 46: 461-467.
- Mars, Messaoud, 2000. Pomegranate plant material: Genetic resources and breeding, a review. in : Melgarejo P. (ed.), Martínez-Nicolás J.J. (ed.), Martínez-Tomé J. (ed.). Production, processing and marketing of pomegranate in the Mediterranean region: Advances in research and technology. Options Méditerranéennes, Série A. Séminaires Méditerranéens: n. 42). pp. 55-62. en ligne au CIHEAM.
- Mars, Messaoud, 2001. Le grenadier (Punica granatum L.). Thèse Montpellier.
- Morton, Julia F., 1987. Fruits of warm climates. Miami. Pomegranate : pp. 352–355. en ligne à New Crop Purdue.
- Seeram, Navindra P., Schulman, Risa N. & Heber, David, 2006. Pomegranates: Ancient Roots to Modern Medicine. CRC Press. (Medicinal and Aromatic Plants – Industrial Profiles).
- Popenoe, Wilson, 1974. Manual of tropical and subtropical fruits. Excluding the banana, coconut, pineapple, citrus frits and fig. Ed. 1 : 1920, Macmillan Company. Reprint 1974, Hafner. Grenadier : pp 375-383.
Liens
- BHL
- California Rare Fruits Growers
- Duke's Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases
- Encyclopedia of Life
- FAO Ecocrop
- Flora of China
- Flora of Pakistan
- Grieve's herbal
- GRIN
- IPNI
- Mansfeld
- Moerman, Native American Ethnobotany
- Multilingual Plant Name Database
- NewCrop Purdue
- Plant List
- Plants for a future
- Pommiers.com
- PROSEA sur Pl@ntUse
- PROTA sur Pl@ntUse
- Pomegranate tree: description and use (projet européen RESGEN29 "Conservation, evaluation, exploitation and collection of minor fruit tree species")
- Tela Botanica
- Wikipédia
- Wikiphyto
- World Agroforestree