Syzygium jambos : Différence entre versions
m (clean up) |
|||
| (13 révisions intermédiaires par 2 utilisateurs non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 1 : | Ligne 1 : | ||
{{Page espèce (plante à graines) | {{Page espèce (plante à graines) | ||
| − | |image = | + | |image = Syzygium jambos Fruit and seeds IMG 4906.JPG |
|légende = | |légende = | ||
| − | |auteur = | + | |auteur = (L.) Alston |
| − | |ordre = | + | |ordre = Myrtales |
| − | |famille = | + | |famille = Myrtaceae |
| − | |genre = | + | |genre = Syzygium |
| − | |nb chromosomes = 2n = | + | |nb chromosomes = 2n = 28, 33, 44, 46, 66 ? |
| − | |origine = | + | |origine = Asie du Sud-Est |
|statut = sauvage ou cultivé | |statut = sauvage ou cultivé | ||
| − | | | + | |français = '''jambosier / jambose''' |
| − | |anglais = '''''' | + | |anglais = '''rose apple''' |
| + | }}{{Encadré | ||
| + | |color=lightgreen | ||
| + | |titre=Résumé des usages | ||
| + | |texte=*fruit comestible cru ou transformé | ||
| + | *fruit distillé : eau de rose | ||
| + | *bois d'œuvre | ||
| + | *bois de feu | ||
| + | *charbon de bois | ||
| + | *médicinal : graines, feuilles, écorce | ||
| + | *ornemental | ||
| + | *arbre d'ombrage | ||
| + | *brise-vent | ||
| + | *mellifère | ||
| + | *écorce : tanin | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
| + | <gallery mode="packed"> | ||
| + | File:Syzygium jambosTree1.jpg|arbre | ||
| + | File:Syzygium jambos 9zz.jpg|tronc | ||
| + | File:Syzygium jambos Foliage and fruit IMG 4901.JPG|feuillage et fruits | ||
| + | File:Syzygium jambos.JPG|fleurs | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
== Noms populaires == | == Noms populaires == | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:100%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:100%;" | ||
| − | + | | français | |
| + | | jambosier / jambose, pomme-rose ; jambrosade, jamrosat (La Réunion) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | anglais | ||
| + | | rose apple, Malabar plum | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | allemand | ||
| + | | Rosenapfel | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | néerlandais | ||
| + | | djamboe mawar | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | italien | ||
| + | | pomarosa, melarosa | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | espagnol | ||
| + | | pomarrosa | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | portugais | ||
| + | | jambo, jambo rosa, jambo amarelo | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | arabe | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | chinois | ||
| + | | 蒲桃 - pu tao (Flora of China) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | sanscrit | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | hindi | ||
| + | | gulabjaman (Wealth of India) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | bengali | ||
| + | | gulabjamb, jamrul (Wealth of India) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | marathi | ||
| + | | gulabjaman (Wealth of India) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | telugu | ||
| + | | jambuneereedu (Wealth of India) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | tamoul | ||
| + | | perunaval, pannirkoyya, sambunaval (Wealth of India) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | kannada | ||
| + | | pannerale (Wealth of India) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | malayalam | ||
| + | | jambavam, malakachampa (Wealth of India) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | oriya | ||
| + | | golabjamli (Wealth of India) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Philippines | ||
| + | | tampoy (tagalog), bunlaun (bisaya), yambo (PROSEA) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Indonésie | ||
| + | | jambu air mawar, jambu mawar, jambu kraton (PROSEA) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Malaysia | ||
| + | | jambu kelampok, jambu mawer (PROSEA) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Thaïlande | ||
| + | | chomphu-namdokmai (centre), manomhom (nord), yamu-panawa (Malay-Yala) (PROSEA) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Vietnam | ||
| + | | ly, bô dào, roi (PROSEA) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Laos | ||
| + | | chièng, kièng (PROSEA) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Cambodge | ||
| + | | châm'-puu (PROSEA) | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | *Voir l'étymologie de [[Etymologie des noms scientifiques#jambos|''jambos'']] et de [[Etymologie des noms scientifiques#jambolana|''jambolana'']]. | ||
== Classification == | == Classification == | ||
| + | ''Syzygium jambos'' (L.) Alston (1931) | ||
| + | |||
| + | synonyme : | ||
| + | *''Eugenia jambos'' L. (1753) | ||
== Cultivars == | == Cultivars == | ||
== Histoire == | == Histoire == | ||
| + | <gallery mode="packed"> | ||
| + | File:Hortus Indicus Malabaricus (Fig. 17) BHL463611.jpg|Malacca-schambu, Rheede 1678, ''Hortus Malabaricus'', vol. 1, pl. 17 | ||
| + | File:Flore médicale des Antilles, ou, Traité des plantes usuelles (Pl. 315) (7795677712).jpg|Descourtilz, 1827. ''Flore médicale des Antilles'', | ||
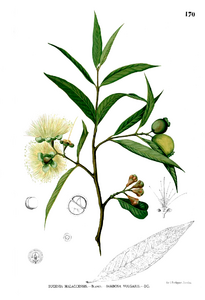
| + | File:Syzygium jambos Blanco1.170.png|Blanco, 1880-1883, ''Flora de Filipinas'' | ||
| + | File:Rose apple (Syzygium jambos (L.) Alston); flowering branch w Wellcome V0042692.jpg|Berthe Hoola van Nooten, XIXe, ''Fleurs, Fruits et Feuillages Choisis de l'Ile de Java'' | ||
| + | File:Rose apple (Syzygium jambos (L.) Alston); fruiting branch wi Wellcome V0042693.jpg|Berthe Hoola van Nooten, XIXe, ''Fleurs, Fruits et Feuillages Choisis de l'Ile de Java'' | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
== Usages == | == Usages == | ||
| + | {{Citation encadré | ||
| + | |texte=Feuillage décoratif. Fleurs à très longues et nombreuses étamines, blanc-jaunâtre, décoratives, malheureusement très caduques et fugaces. Brise-vents en Dominique. | ||
| + | |auteur=Rollet, 2010. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{Citation encadré | ||
| + | |texte= Abundantly cultivated in all tropical regions for its edible fruit, also as ornamental or shade tree and wind break. The fruits are eaten raw by children or are stewed as dessert. They are seldom sold in markets because of their lack of a distinct flavour. With lemon juice they are prepared to jam or jelly and more frequently preserved mixed with other fruits, also prepared to sauces and syrup or candied with cinnamon. Bark, leaves and seeds are medicinally used. The bark is sometimes used locally for tanning. | ||
| + | |auteur=Mansfeld. | ||
| + | }} | ||
== Références == | == Références == | ||
| + | *Boym, Michał, 1696. ''Flora Sinensis''. Paris, 15 p. Seconde édition en français. Voir [[Flora Sinensis, 1696#Giam-bo|Giam-bo]] sur Pl@ntUse. | ||
| + | *Chauvet, Michel, 2018. ''[[Encyclopédie des plantes alimentaires]]''. Paris, Belin. 880 p. (p. 496) | ||
| + | *Rollet, Bernard et coll., 2010. ''Arbres des Petites Antilles''. Tome 1 : ''Introduction à la dendrologie''. 276 p. Tome 2 : ''Description des espèces''. 866 p. + 46 pl. coul. + CD de photos sur l'anatomie du bois. Basse-Terre, ONF. Voir [[Syzygium jambos (Rollet, Antilles)|sur Pl@ntUse]]. | ||
== Liens == | == Liens == | ||
*[http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/search.aspx?SearchTerm=Syzygium%20jambos&SearchCat= BHL] | *[http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/search.aspx?SearchTerm=Syzygium%20jambos&SearchCat= BHL] | ||
*[http://ecocrop.fao.org/ecocrop/srv/en/cropFindForm FAO Ecocrop] | *[http://ecocrop.fao.org/ecocrop/srv/en/cropFindForm FAO Ecocrop] | ||
| − | *[ | + | *[https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=50070 GRIN] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
*[http://www.ipni.org/ipni/simplePlantNameSearch.do?find_wholeName=Syzygium%20jambos&output_format=normal&query_type=by_query&back_page=query_ipni.html IPNI] | *[http://www.ipni.org/ipni/simplePlantNameSearch.do?find_wholeName=Syzygium%20jambos&output_format=normal&query_type=by_query&back_page=query_ipni.html IPNI] | ||
| − | *[http://mansfeld.ipk-gatersleben.de/ | + | *[http://mansfeld.ipk-gatersleben.de/apex/f?p=185:46:6754362930794::NO::module,mf_use,source,akzanz,rehm,akzname,taxid:mf,,botnam,0,,Syzygium%20jambos,12364 Mansfeld] |
| − | + | ||
*[http://www.plantnames.unimelb.edu.au/Sorting/Syzygium.html Multilingual Plant Name Database] | *[http://www.plantnames.unimelb.edu.au/Sorting/Syzygium.html Multilingual Plant Name Database] | ||
| − | *[ | + | *[https://hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/nexus/Syzygium_jambos_nex.html NewCrop Purdue] |
*[http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/search?q=Syzygium+jambos Plant List] | *[http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/search?q=Syzygium+jambos Plant List] | ||
*[http://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Syzygium%20jambos Plants for a future] | *[http://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Syzygium%20jambos Plants for a future] | ||
*[[:en:Syzygium jambos (PROSEA)|PROSEA sur Pl@ntUse]] | *[[:en:Syzygium jambos (PROSEA)|PROSEA sur Pl@ntUse]] | ||
| − | *[ | + | *[https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/447411/tab/taxo TAXREF] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
*[http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Syzygium%20jambos Useful Tropical Plants Database] | *[http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Syzygium%20jambos Useful Tropical Plants Database] | ||
*[https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syzygium%20jambos Wikipédia] | *[https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Syzygium%20jambos Wikipédia] | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | [[Category:Syzygium]] | ||
Version actuelle en date du 27 septembre 2020 à 18:28
Syzygium jambos (L.) Alston
| Ordre | Myrtales |
|---|---|
| Famille | Myrtaceae |
| Genre | Syzygium |
2n = 28, 33, 44, 46, 66 ?
Origine : Asie du Sud-Est
sauvage ou cultivé
| Français | jambosier / jambose |
|---|---|
| Anglais | rose apple |
- fruit comestible cru ou transformé
- fruit distillé : eau de rose
- bois d'œuvre
- bois de feu
- charbon de bois
- médicinal : graines, feuilles, écorce
- ornemental
- arbre d'ombrage
- brise-vent
- mellifère
- écorce : tanin
Sommaire
Description
Noms populaires
| français | jambosier / jambose, pomme-rose ; jambrosade, jamrosat (La Réunion) |
| anglais | rose apple, Malabar plum |
| allemand | Rosenapfel |
| néerlandais | djamboe mawar |
| italien | pomarosa, melarosa |
| espagnol | pomarrosa |
| portugais | jambo, jambo rosa, jambo amarelo |
| arabe | |
| chinois | 蒲桃 - pu tao (Flora of China) |
| sanscrit | |
| hindi | gulabjaman (Wealth of India) |
| bengali | gulabjamb, jamrul (Wealth of India) |
| marathi | gulabjaman (Wealth of India) |
| telugu | jambuneereedu (Wealth of India) |
| tamoul | perunaval, pannirkoyya, sambunaval (Wealth of India) |
| kannada | pannerale (Wealth of India) |
| malayalam | jambavam, malakachampa (Wealth of India) |
| oriya | golabjamli (Wealth of India) |
| Philippines | tampoy (tagalog), bunlaun (bisaya), yambo (PROSEA) |
| Indonésie | jambu air mawar, jambu mawar, jambu kraton (PROSEA) |
| Malaysia | jambu kelampok, jambu mawer (PROSEA) |
| Thaïlande | chomphu-namdokmai (centre), manomhom (nord), yamu-panawa (Malay-Yala) (PROSEA) |
| Vietnam | ly, bô dào, roi (PROSEA) |
| Laos | chièng, kièng (PROSEA) |
| Cambodge | châm'-puu (PROSEA) |
Classification
Syzygium jambos (L.) Alston (1931)
synonyme :
- Eugenia jambos L. (1753)
Cultivars
Histoire
Usages
Feuillage décoratif. Fleurs à très longues et nombreuses étamines, blanc-jaunâtre, décoratives, malheureusement très caduques et fugaces. Brise-vents en Dominique.
Abundantly cultivated in all tropical regions for its edible fruit, also as ornamental or shade tree and wind break. The fruits are eaten raw by children or are stewed as dessert. They are seldom sold in markets because of their lack of a distinct flavour. With lemon juice they are prepared to jam or jelly and more frequently preserved mixed with other fruits, also prepared to sauces and syrup or candied with cinnamon. Bark, leaves and seeds are medicinally used. The bark is sometimes used locally for tanning.
Références
- Boym, Michał, 1696. Flora Sinensis. Paris, 15 p. Seconde édition en français. Voir Giam-bo sur Pl@ntUse.
- Chauvet, Michel, 2018. Encyclopédie des plantes alimentaires. Paris, Belin. 880 p. (p. 496)
- Rollet, Bernard et coll., 2010. Arbres des Petites Antilles. Tome 1 : Introduction à la dendrologie. 276 p. Tome 2 : Description des espèces. 866 p. + 46 pl. coul. + CD de photos sur l'anatomie du bois. Basse-Terre, ONF. Voir sur Pl@ntUse.