Pimenta dioica : Différence entre versions
De PlantUse Français
| (6 révisions intermédiaires par le même utilisateur non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 32 : | Ligne 32 : | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width:100%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width:100%;" | ||
| français | | français | ||
| − | | piment Jamaïque, toute-épice, piment couronné | + | | piment Jamaïque, toute-épice, piment couronné ; bois d’Inde citronnelle (Ste-Lucie), malaguette, poivre-Jamaïque (Haïti) (Rollet) |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | créole antillais | ||
| + | | bwadenon (TRAMIL) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| anglais | | anglais | ||
| Ligne 47 : | Ligne 50 : | ||
|- | |- | ||
| espagnol | | espagnol | ||
| − | | pimienta de Jamaica ; pimienta gorda, pimienta de Tabasco, pimienta de Chiapas (Mexique) | + | | pimienta de Jamaica ; pimienta gorda, pimienta de Tabasco, pimienta de Chiapas (Mexique), pimento ; malagueta (Saint-Domingue) (TRAMIL) |
|- | |- | ||
| portugais | | portugais | ||
| Ligne 75 : | Ligne 78 : | ||
== Usages == | == Usages == | ||
| + | {{Citation encadré | ||
| + | |texte=Cultivated mainly in Jamaica, Guatemala and Mexico (Yucatán), also in northern South America, India and Réunion. The unripe dried fruits contain 3,3-5,0% etheric oil and are worldwide frequently used as spice. The leaves contain also etheric oil (Pimenta leaf oil), which is mainly used in the perfumery. Leaves and fruits serve in the folk medicine. | ||
| + | |auteur=Mansfeld. | ||
| + | }} | ||
== Références == | == Références == | ||
*Chauvet, Michel, 2018. ''[[Encyclopédie des plantes alimentaires]]''. Paris, Belin. 880 p. (p. 488) | *Chauvet, Michel, 2018. ''[[Encyclopédie des plantes alimentaires]]''. Paris, Belin. 880 p. (p. 488) | ||
| + | *Rollet, Bernard et coll., 2010. ''Arbres des Petites Antilles''. Tome 1 : ''Introduction à la dendrologie''. 276 p. Tome 2 : ''Description des espèces''. 866 p. + 46 pl. coul. + CD de photos sur l'anatomie du bois. Basse-Terre, ONF. Voir [[Pimenta dioica (Rollet, Antilles)|sur Pl@ntUse]]. | ||
| + | *TRAMIL, ''Pharmacopée végétale caribéenne'', éd. scient. L. Germosén-Robineau. 2014. 3e éd. Santo Domingo, Canopé de Guadeloupe. 420 p. Voir sur [[Pimenta dioica (TRAMIL)|Pl@ntUse]] | ||
== Liens == | == Liens == | ||
*[http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/search.aspx?SearchTerm=Pimenta%20dioica&SearchCat= BHL] | *[http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/search.aspx?SearchTerm=Pimenta%20dioica&SearchCat= BHL] | ||
*[http://ecocrop.fao.org/ecocrop/srv/en/cropFindForm FAO Ecocrop] | *[http://ecocrop.fao.org/ecocrop/srv/en/cropFindForm FAO Ecocrop] | ||
| + | *[http://gernot-katzers-spice-pages.com/engl/Pime_dio.html Gernot Katzer's Spice pages] | ||
*[http://botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/a/allsp025.html Grieve's herbal] | *[http://botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/a/allsp025.html Grieve's herbal] | ||
| − | *[ | + | *[https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomydetail.aspx?id=28390 GRIN] |
*[http://www.ipni.org/ipni/simplePlantNameSearch.do?find_wholeName=Pimenta%20dioica&output_format=normal&query_type=by_query&back_page=query_ipni.html IPNI] | *[http://www.ipni.org/ipni/simplePlantNameSearch.do?find_wholeName=Pimenta%20dioica&output_format=normal&query_type=by_query&back_page=query_ipni.html IPNI] | ||
*[http://mansfeld.ipk-gatersleben.de/apex/f?p=185:46:7997762968513::NO::module,mf_use,source,akzanz,rehm,akzname,taxid:mf,,botnam,0,,Pimenta%20dioica,12263 Mansfeld] | *[http://mansfeld.ipk-gatersleben.de/apex/f?p=185:46:7997762968513::NO::module,mf_use,source,akzanz,rehm,akzname,taxid:mf,,botnam,0,,Pimenta%20dioica,12263 Mansfeld] | ||
| Ligne 90 : | Ligne 100 : | ||
*[http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/search?q=Pimenta+dioica Plant List] | *[http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/search?q=Pimenta+dioica Plant List] | ||
*[[:en:Pimenta dioica (PROSEA)|PROSEA sur Pl@ntUse]] | *[[:en:Pimenta dioica (PROSEA)|PROSEA sur Pl@ntUse]] | ||
| − | *[ | + | *[https://inpn.mnhn.fr/espece/cd_nom/706657/tab/taxo TAXREF] |
*[http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Pimenta%20dioica Useful Tropical Plants Database] | *[http://tropical.theferns.info/viewtropical.php?id=Pimenta%20dioica Useful Tropical Plants Database] | ||
*[https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pimenta%20dioica Wikipédia] | *[https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pimenta%20dioica Wikipédia] | ||
Version actuelle en date du 9 décembre 2020 à 11:51
Pimenta dioica (L.) Merr.
| Ordre | Myrtales |
|---|---|
| Famille | Myrtaceae |
| Genre | Pimenta |
2n = 22
Origine : Mésoamérique, Grandes Antilles
sauvage ou cultivé
| Français | toute-épice |
|---|---|
| Anglais | allspice |
Résumé des usages
- fruit : épice
- fruit : ingrédient de boissons et de liqueurs
- feuille : épice
- tiges utilisées pour des cannes
- médicinal
Sommaire
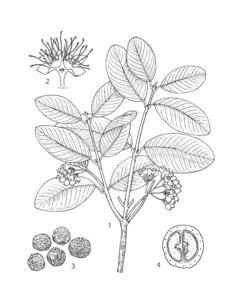
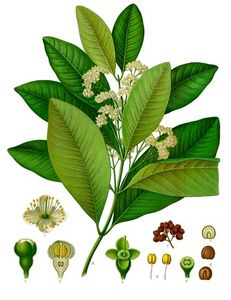
Description
Noms populaires
| français | piment Jamaïque, toute-épice, piment couronné ; bois d’Inde citronnelle (Ste-Lucie), malaguette, poivre-Jamaïque (Haïti) (Rollet) |
| créole antillais | bwadenon (TRAMIL) |
| anglais | allspice, pimento, Jamaica pepper |
| allemand | Piment, Nelkenpfeffer ; Neugewürz (Autriche) |
| néerlandais | piment |
| italien | pepe della Giamaica, pimento |
| espagnol | pimienta de Jamaica ; pimienta gorda, pimienta de Tabasco, pimienta de Chiapas (Mexique), pimento ; malagueta (Saint-Domingue) (TRAMIL) |
| portugais | pimenta da Jamaica |
| arabe |
Classification
Pimenta dioica (L.) Merr. (1947)
basionyme :
- Myrtus dioica L. (1759)
synonymes :
- Myrtus pimenta L. (1753)
- Pimenta officinalis Lindl. (1821)
Cultivars
Histoire
Usages
Cultivated mainly in Jamaica, Guatemala and Mexico (Yucatán), also in northern South America, India and Réunion. The unripe dried fruits contain 3,3-5,0% etheric oil and are worldwide frequently used as spice. The leaves contain also etheric oil (Pimenta leaf oil), which is mainly used in the perfumery. Leaves and fruits serve in the folk medicine.
Mansfeld.
Références
- Chauvet, Michel, 2018. Encyclopédie des plantes alimentaires. Paris, Belin. 880 p. (p. 488)
- Rollet, Bernard et coll., 2010. Arbres des Petites Antilles. Tome 1 : Introduction à la dendrologie. 276 p. Tome 2 : Description des espèces. 866 p. + 46 pl. coul. + CD de photos sur l'anatomie du bois. Basse-Terre, ONF. Voir sur Pl@ntUse.
- TRAMIL, Pharmacopée végétale caribéenne, éd. scient. L. Germosén-Robineau. 2014. 3e éd. Santo Domingo, Canopé de Guadeloupe. 420 p. Voir sur Pl@ntUse