Prosopis juliflora
Prosopis juliflora (Sw.) DC.
| Ordre | Fabales |
|---|---|
| Famille | Fabaceae |
| Genre | Prosopis |
2n =
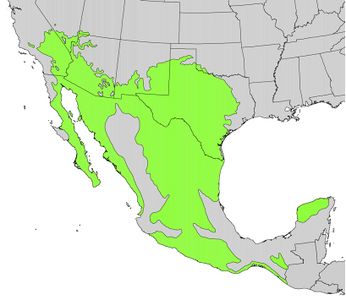
Origine : Etats-Unis,
du Mexique à la Colombie
sauvage ou cultivé
| Français | bayahonde |
|---|---|
| Anglais | mesquite |
- bois d'œuvre : piquets
- ornemental
- utilisé en reforestation et fixation des dunes
- mellifère
- fourrage : gousses
- jeunes fruits et pousses consommés
- fruit : boisson fermentée
- gomme extraite de l'albumen
- gomme exsudée de l'écorce
- écorce : tanin
Sommaire
Description
Noms populaires
| français | bayahonde |
| créole antillais | bayawonn, bayarone, bayahonde (TRAMIL) |
| créole haïtien | bayawond blan (TRAMIL) |
| anglais | mesquite (Etats-Unis) (Rollet) ; long-thorn kiawe (Hawaii) |
| espagnol | mesquite (Mexique, Trinidad) (Rollet) ; algarrobo, mezquite |
| portugais | algarobeira, pé-de-algaroba, algarobo |
Classification
Prosopis juliflora (Sw.) DC. (1825)
basionyme :
- Mimosa juliflora Sw. (1788)
Cultivars
Histoire
Usages
Piquets de clôtures, traverses. Arbre d’ornement, très mellifère, fruit mangé par le bétail et les enfants.
Planted especially for its nutritious pods, for honey and "mesquite gum" production (Chile) in tropical and subtropical areas of America (Peru, Chile, Paraguay, Brazil), in Africa, Asia (India, Pakistan) and Australia. Used for protection of Eucalyptus in Australia. Cultivated for afforestation of dry desert areas and for fixing of sand dunes. Cooked pods are eaten with young shoots or are used as fodder. South American inhabitants prepare an alcoholic drink of the fruit ("alole", "vino mezquite"). The ground endosperm is "mesquite gum", a galactomannan-type polysaccharid. The bark is used as tanning material and exudates a gum, similar to gum arabic. The tree is expanding fast in the South states of the USA ("national weed") and has to be eradicated.
Références
- Bekele-Tesemma, Azene, 2007. Useful trees and shrubs for Ethiopia. Identification, propagation and management for 17 agroclimatic zones. Nairobi, ICRAF - RELMA. 550 p. (Technical Manual 6). Voir l'article
- Rollet, Bernard et coll., 2010. Arbres des Petites Antilles. Tome 1 : Introduction à la dendrologie. 276 p. Tome 2 : Description des espèces. 866 p. + 46 pl. coul. + CD de photos sur l'anatomie du bois. Basse-Terre, ONF. Voir sur Pl@ntUse.
- TRAMIL, Pharmacopée végétale caribéenne, éd. scient. L. Germosén-Robineau. 2014. 3e éd. Santo Domingo, Canopé de Guadeloupe. 420 p. Voir sur Pl@ntUse