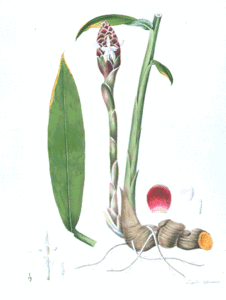
Zingiber montanum
Zingiber montanum
(J. Koenig) Link ex A. Dietr.
| Ordre | Zingiberales |
|---|---|
| Famille | Zingiberaceae |
| Genre | Zingiber |
2n =
Origine : Inde, Bangladesh, Vietnam, Laos
sauvage et cultivé
| Français | gingembre marron |
|---|---|
| Anglais | cassumunar ginger |
Résumé des usages
- rhizome aromatique (susbstitut du gingembre)
- médicinal (rhizome)
- source d'un poison de flèche
- planté pour protéger les rizières des animaux, qui évitent la plante
Description
jeunes inflorescences (Dorami Chan)
fleur (Jayesh Pail)
- plante herbacée de 2 m de haut
- rhizome volumineux, oblong, articulé, strié, de couleur orange foncé en dedans
- feuilles presque sessiles, linéaires-lancéolées, longues de 20-40 cm, vert-foncé et glabres en dessus, vert-pâle et velues en dessous
- hampe latérale, haute de 20-40 cm, embrassée par des écailles engainantes et velues
- inflorescence : cône oblong, long de 11 cm
- bractées larges, ferrugineuses, avec le bord plus pâle et membraneux, velues
- fleurs jaune-soufre, fugaces
Noms populaires
| français | gingembre marron (PROSEA) |
| créole antillais | tjitjima (TRAMIL) |
| anglais | cassumunar ginger, bengal root (PROSEA) |
| allemand | Blockzitwer, gelber Zitwer (Mansfeld) |
| espagnol | jengibre amargo (Saint-Domingue) |
| sanscrit | vanardraka (Wealth of India) |
| hindi | banada (Wealth of India) ; बनअदरक - banadrak (Mansfeld) |
| bengali | banada (Wealth of India) ; banadrak (Mansfeld) |
| marathi | nisan, penlekosht (Wealth of India) |
| telugu | karraallamu, karrapasupu (Wealth of India) |
| kannada | kadushunti (Wealth of India) |
| oriya | banooda, vanardraka (Wealth of India) |
| Indonésie | banglai (général), bengle (javanais), panglay (sundanais) (PROSEA) |
| Malaysia | bunglai, bangle, bolai (PROSEA) |
| thai | puloei (nord), phlai (centre), wan-fai (centre) (PROSEA) |
| vietnamien | gừng dại, gừng dỏ (PROSEA) |
| Laos | hva:nz ph'ai, hva:nz kè:z hva:nz (PROSEA) |
Classification
Zingiber montanum (J. Koenig) Link ex A. Dietr. (1831)
basionyme :
- Amomum montanum J. Koenig (1783)
synonyme :
- Zingiber purpureum Roscoe (1807)
- Zingiber cassumunar Roxb. (1810)
Cultivars
Histoire
Usages
In tropical Asia cultivated in many places (e.g. India, Bangladesh, Malaysia, Thailand, Java). The rhizomes serve medicinal purposes (occasionally as a substitute for Zingiber officinale Roscoe). The species is also used for making arrow poison. The plant, avoided by animals, is planted for protection on the edge of rice fields.
Mansfeld.
Références
- IBPGR, 1981. Root and tuber crops. Rome, IBPGR Secretariat. 107 p.
- Burkill, I. H., 1966. A dictionary of the economic products of the Malay Peninsula. 2 Vols. Kuala Lumpur, Ministry Agric. & Cooperatives. 2444 p.
- Chakravarti, H. L. & D. P. Chakraborty, 1964. Spices of India. Indian Agriculturist, 8(2) : 124-177.
- Duong, Nguyen Van, 1993. Medicinal plants of Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos. Self Publ. 528 pp.
- TRAMIL, Pharmacopée végétale caribéenne, éd. scient. L. Germosén-Robineau. 2014. 3e éd. Santo Domingo, Canopé de Guadeloupe. 420 p. Voir sur Pl@ntUse
- Wealth of India (The), 1976. A dictionary of Indian raw materials and industrial products. New-Delhi, Council of scientific and industrial research. Vol. 11. Raw materials : X-Z and cumulative indexes. XXVIII-385 p. Reprinted 2005.