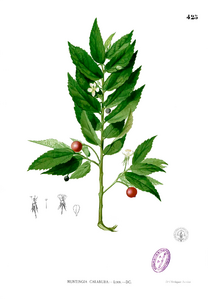
Muntingia calabura
De PlantUse Français
Muntingia calabura L.
| Ordre | Malvales |
|---|---|
| Famille | Muntingiaceae |
| Genre | Muntingia |
2n = 28
Origine : Amérique tropicale
sauvage et cultivé
| Français | |
|---|---|
| Anglais |
Résumé des usages
- fruit comestible
- arbre d'alignement
- ornemental
- bois de feu
- écorce : cordes
- médicinal : fleurs
Sommaire
Description
Noms populaires
| français | bois d'orme (Mansfeld) |
| anglais | capulin, Jamaica cherry ; Chinese cherry, Japanese cherry, Panama berry, strawberry tree (Mansfeld) |
| espagnol | capulín, cereza, chitato, pasito (Colombie), yumanaza, cerezo caspi (Pérou) (Mansfeld) |
| portugais | calabura, páo de seda (Brésil) |
| Philippines | datiles (PROSEA) |
| Indonésie | cerri, kersen, talok (Java) (PROSEA) |
| Malaysia | kerukup siam (PROSEA) ; buah cheri (Mansfeld) |
| Thaïlande | takhop farang (PROSEA) |
| Vietnam | trúng cá, mât sâm (PROSEA) |
| Laos | khoom sômz, takhôb (PROSEA) |
| Cambodge | krâkhôb barang (PROSEA) |
Classification
Muntingia calabura L. (1753)
Cultivars
Histoire
Usages
It is naturalized in SE Asia an the Philippines and cultivated in tropical regions all over the world. The sweet berries are a savoury fruit and the bark fibres used to make rope. Sometimes it is cultivated as ornamental tree.
Mansfeld.
Références
- Morton, Julia F., 1987. Jamaica Cherry. p. 65–69. In: Fruits of warm climates. Miami, Floride. sur NewCrop Purdue
- Rollet, Bernard et coll., 2010. Arbres des Petites Antilles. Tome 1 : Introduction à la dendrologie. 276 p. Tome 2 : Description des espèces. 866 p. + 46 pl. coul. + CD de photos sur l'anatomie du bois. Basse-Terre, ONF. Voir sur Pl@ntUse.