Blitum bonus-henricus : Différence entre versions
De PlantUse Français
| (18 révisions intermédiaires par 2 utilisateurs non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 2 : | Ligne 2 : | ||
|image = Chenopodium bonus-henricus.JPG | |image = Chenopodium bonus-henricus.JPG | ||
|légende = | |légende = | ||
| − | |auteur = | + | |auteur = (L.) C.A. Mey. |
|ordre = Caryophyllales | |ordre = Caryophyllales | ||
|famille = Amaranthaceae | |famille = Amaranthaceae | ||
|genre = Blitum | |genre = Blitum | ||
| − | |nb chromosomes = 2n = | + | |nb chromosomes = 2n = 32, 36 |
| − | |origine = | + | |origine = Europe |
|statut = sauvage et cultivé | |statut = sauvage et cultivé | ||
| + | |français = '''bon-henri''' | ||
| + | |anglais = '''Good King Henry''' | ||
| + | }}{{Encadré | ||
| + | |color=lightgreen | ||
| + | |titre=Résumé des usages | ||
| + | |texte=*légume : | ||
| + | **feuilles cuites comme les épinards ; | ||
| + | **jeunes pousses comme les asperges | ||
| + | *médicinal | ||
}} | }} | ||
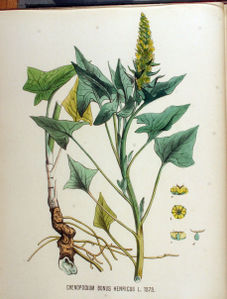
| − | * | + | == Description == |
| − | * | + | *plante herbacée érigée, peu ramifiée, pulvérulente, inodore, de 20-70 cm de haut |
| − | + | *feuilles pétiolées, triangulaires hastées, plus ou moins entières, de 4,5-10 cm de long | |
| − | + | *inflorescence : grappe d'épis de glomérules, feuillée seulement à la base | |
| − | + | *fruit : achène obovoïde, enserré dans le périanthe | |
| + | <gallery mode="packed"> | ||
| + | File:Chenopodium bonus-henricus02.jpg|plante en fleurs | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
== Noms populaires == | == Noms populaires == | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" style="width:100%;" | |
| − | = | + | | français |
| − | + | | bon-henri, épinard sauvage, toute-bonne | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | anglais | |
| + | | Good King Henry, allgood, perennial spinach, wild spinach, fat hen | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | allemand | ||
| + | | guter Heinrich, Hundsmelde, wilder Spinat | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | néerlandais | ||
| + | | brave Hendrik, algoede | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | italien | ||
| + | | buono Enrico, buonenrico, tuttabuona ; olaci (l’Aquila) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | espagnol | ||
| + | | buen Enrique, zurrón | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | *Voir les noms de la [[Chenopodium (Rolland, Flore populaire)#Chenopodium bonus henricus|''Flore populaire'' d'Eugène Rolland]] | ||
| + | *Voir les [http://www.meertens.knaw.nl/pland/woordenboekartikel.php?term=Brave%20Hendrik noms néerlandais] de ''Plantennamen in de Nederlandse Dialecten'' (PLAND) | ||
== Classification == | == Classification == | ||
| + | ''Blitum bonus-henricus'' (L.) C.A. Mey. (1829) | ||
| + | |||
| + | basionyme : | ||
| + | *''Chenopodium bonus-henricus'' L. (1753) | ||
== Cultivars == | == Cultivars == | ||
== Histoire == | == Histoire == | ||
| − | <gallery | + | <gallery mode="packed"> |
| + | File:Güter Heinrich Fuchs 1543 463.jpg|Güter Heinrich [[Fuchs, New Kreüterbuch, illustrations|Fuchs, 1543. ''New Kreüterbuch'']] | ||
File:Illustration Chenopodium bonus-henricus0 clean.JPG|Thomé, 1885, ''Flora von Deutschland'' | File:Illustration Chenopodium bonus-henricus0 clean.JPG|Thomé, 1885, ''Flora von Deutschland'' | ||
File:Chenopodium bonus-henricus — Flora Batava — Volume v18.jpg|''Flora Batava'', 1889 | File:Chenopodium bonus-henricus — Flora Batava — Volume v18.jpg|''Flora Batava'', 1889 | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Le bon-henri a été très cultivé et consommé avant l'arrivée de l'épinard. Il est maintenant pratiquement abandonné, et subsiste comme adventice près des chalets de montagne. | ||
== Usages == | == Usages == | ||
| + | *Voir les [[Arroche bon-henri (Vilmorin-Andrieux, 1904)|''Plantes potagères'' de Vilmorin (1904)]] | ||
| + | *Voir les [[Bon-Henri (Cazin 1868)|''Plantes médicinales'' de Cazin (1868)]] | ||
| + | *Voir [[:en:Chenopodium (Sturtevant, 1919)#Chenopodium bonus-henricus Linn.|''Edible plants'' de Sturtevant (1919)]] | ||
== Références == | == Références == | ||
| + | *Becker-Dillingen, J., 1924. ''Handbuch des gesamten Gemüsebaues''. (2nd ed. 1929, 5th ed. 1950, 6th ed. 1956). Berlin, Parey. 1065 p. | ||
| + | *Chauvet, Michel, 2018. [[Encyclopédie des plantes alimentaires|''Encyclopédie des plantes alimentaires'']]. Paris, Belin. 880 p. (p. 30) | ||
| + | *Fischer-Benzon, R. von, 1894. ''Altdeutsche Gartenflora - Untersuchungen über die Nutzpflanzen des deutschen Mittelalters, ihre Wanderung und ihre Vorgeschichte im klassischen Altertum''. Kiel, Lipsius & Tischer. 254 p. | ||
== Liens == | == Liens == | ||
*[http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/search.aspx?SearchTerm=Blitum%20bonus-henricus&SearchCat= BHL] | *[http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/search.aspx?SearchTerm=Blitum%20bonus-henricus&SearchCat= BHL] | ||
| − | *[http://ecocrop.fao.org/ecocrop/srv/en/cropView?id=4485 Ecocrop] | + | *[http://ecocrop.fao.org/ecocrop/srv/en/cropView?id=4485 Ecocrop] (''Chenopodium bonus-henricus'') |
| − | *[http://botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/g/goosef30.html#goo Grieve's herbal] | + | *[http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=242415396 ''Flora of North America''] (''Chenopodium bonus-henricus'') |
| + | *[http://botanical.com/botanical/mgmh/g/goosef30.html#goo Grieve's herbal] (''Chenopodium bonus-henricus'') | ||
*[http://www.ars-grin.gov/cgi-bin/npgs/html/tax_search.pl?Blitum%20bonus-henricus GRIN] | *[http://www.ars-grin.gov/cgi-bin/npgs/html/tax_search.pl?Blitum%20bonus-henricus GRIN] | ||
*[http://www.ipni.org/ipni/simplePlantNameSearch.do?find_wholeName=Blitum%20bonus-henricus&output_format=normal&query_type=by_query&back_page=query_ipni.html IPNI] | *[http://www.ipni.org/ipni/simplePlantNameSearch.do?find_wholeName=Blitum%20bonus-henricus&output_format=normal&query_type=by_query&back_page=query_ipni.html IPNI] | ||
| − | *[http://mansfeld.ipk-gatersleben.de/pls/htmldb_pgrc/f?p=185:45:1329164412874601::NO::P7_BOTNAME,P7_DB_CHECKBOX1,P7_DB_CHECKBOX2,P7_DB_CHECKBOX4: | + | *[http://mansfeld.ipk-gatersleben.de/pls/htmldb_pgrc/f?p=185:45:1329164412874601::NO::P7_BOTNAME,P7_DB_CHECKBOX1,P7_DB_CHECKBOX2,P7_DB_CHECKBOX4:Chenopodium%20bonus-henricus,,, Mansfeld] (''Chenopodium bonus-henricus'') |
| − | + | ||
*[http://www.plantnames.unimelb.edu.au/Sorting/Blitum.html Multilingual Plant Name Database] | *[http://www.plantnames.unimelb.edu.au/Sorting/Blitum.html Multilingual Plant Name Database] | ||
| − | *[http://www.hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/ | + | *[http://www.hort.purdue.edu/newcrop/Crops/GoodKingHenry.html NewCrop Purdue] |
*[http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/search?q=Blitum+bonus-henricus Plant List] | *[http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl1.1/search?q=Blitum+bonus-henricus Plant List] | ||
| − | *[http://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Chenopodium+bonus-henricus Plants for a future] | + | *[http://pfaf.org/user/Plant.aspx?LatinName=Chenopodium+bonus-henricus Plants for a future] (''Chenopodium bonus-henricus'') |
| − | + | *[http://www.tela-botanica.org/bdtfx-nn-9905 Tela Botanica] | |
| − | *[http://www.tela-botanica.org/ | + | *[https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chenopodium%20bonus-henricus Wikipédia] (''Chenopodium bonus-henricus'') |
| − | *[https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/ | + | |
[[Category:Blitum]] | [[Category:Blitum]] | ||
| + | [[Catégorie: Légume tempéré, sauvage]] | ||
| + | [[Catégorie: Médecine humaine, tempéré secondaire]] | ||
Version actuelle en date du 26 octobre 2020 à 09:53
Blitum bonus-henricus (L.) C.A. Mey.
| Ordre | Caryophyllales |
|---|---|
| Famille | Amaranthaceae |
| Genre | Blitum |
2n = 32, 36
Origine : Europe
sauvage et cultivé
| Français | bon-henri |
|---|---|
| Anglais | Good King Henry |
Résumé des usages
- légume :
- feuilles cuites comme les épinards ;
- jeunes pousses comme les asperges
- médicinal
Sommaire
Description
- plante herbacée érigée, peu ramifiée, pulvérulente, inodore, de 20-70 cm de haut
- feuilles pétiolées, triangulaires hastées, plus ou moins entières, de 4,5-10 cm de long
- inflorescence : grappe d'épis de glomérules, feuillée seulement à la base
- fruit : achène obovoïde, enserré dans le périanthe
Noms populaires
| français | bon-henri, épinard sauvage, toute-bonne |
| anglais | Good King Henry, allgood, perennial spinach, wild spinach, fat hen |
| allemand | guter Heinrich, Hundsmelde, wilder Spinat |
| néerlandais | brave Hendrik, algoede |
| italien | buono Enrico, buonenrico, tuttabuona ; olaci (l’Aquila) |
| espagnol | buen Enrique, zurrón |
- Voir les noms de la Flore populaire d'Eugène Rolland
- Voir les noms néerlandais de Plantennamen in de Nederlandse Dialecten (PLAND)
Classification
Blitum bonus-henricus (L.) C.A. Mey. (1829)
basionyme :
- Chenopodium bonus-henricus L. (1753)
Cultivars
Histoire
Güter Heinrich Fuchs, 1543. New Kreüterbuch
Le bon-henri a été très cultivé et consommé avant l'arrivée de l'épinard. Il est maintenant pratiquement abandonné, et subsiste comme adventice près des chalets de montagne.
Usages
- Voir les Plantes potagères de Vilmorin (1904)
- Voir les Plantes médicinales de Cazin (1868)
- Voir Edible plants de Sturtevant (1919)
Références
- Becker-Dillingen, J., 1924. Handbuch des gesamten Gemüsebaues. (2nd ed. 1929, 5th ed. 1950, 6th ed. 1956). Berlin, Parey. 1065 p.
- Chauvet, Michel, 2018. Encyclopédie des plantes alimentaires. Paris, Belin. 880 p. (p. 30)
- Fischer-Benzon, R. von, 1894. Altdeutsche Gartenflora - Untersuchungen über die Nutzpflanzen des deutschen Mittelalters, ihre Wanderung und ihre Vorgeschichte im klassischen Altertum. Kiel, Lipsius & Tischer. 254 p.
Liens
- BHL
- Ecocrop (Chenopodium bonus-henricus)
- Flora of North America (Chenopodium bonus-henricus)
- Grieve's herbal (Chenopodium bonus-henricus)
- GRIN
- IPNI
- Mansfeld (Chenopodium bonus-henricus)
- Multilingual Plant Name Database
- NewCrop Purdue
- Plant List
- Plants for a future (Chenopodium bonus-henricus)
- Tela Botanica
- Wikipédia (Chenopodium bonus-henricus)