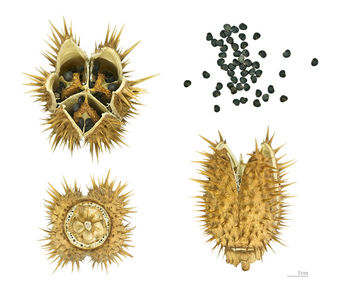
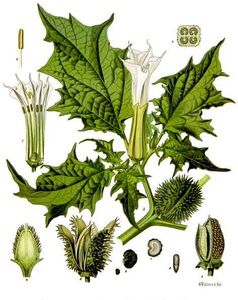
Datura stramonium
Datura stramonium L.
| Ordre | Solanales |
|---|---|
| Famille | Solanaceae |
| Genre | Datura |
2n =
Origine : Mexique ?
sauvage ou cultivé
| Français | ' |
|---|---|
| Anglais | ' |
- médicinal ; psychotrope
Sommaire
Description
Noms populaires
| français | stramoine, pomme épineuse, datura, feuille du diable, herbe du diable (PROTA) |
| anglais | thorn apple, green thorn apple, jimsonweed, Jamestown weed, devil’s apple, devil’s trumpet, stramonium (PROTA) |
| allemand | |
| néerlandais | |
| italien | |
| espagnol | |
| portugais | figueira do inferno, pomo espinhoso, erva dos bruxos, palha verde, estramonio (PROTA) |
| arabe | |
| swahili | muranha (PROTA) |
| chinois | 曼陀罗 - man tuo luo (Flora of China) |
| sanscrit | dhattura, unmatta, kanaka, shivapriya (Wealth of India) |
| hindi | dhatura (Wealth of India) |
| bengali | dhatura (Wealth of India) |
| marathi | dhatura (Wealth of India) |
| gujerati | dhatura (Wealth of India) |
| telugu | ummatta (Wealth of India) |
| tamoul | ummatta (Wealth of India) |
| kannada | ಬಿಳಿಉಮ್ಮತ್ತಿ - bili ummatti, ಉಂಬತ್ತಿ - umbatti, ದತ್ತವ - dattava, ದತ್ತೂರಿ - dattoori ಸದಾದತ್ತೂರ - sadaa dattoora, ಧತ್ತೂರಿ - dhattoori, ಧುಸ್ತೂರ - dhustoora, ಮದ್ದುಗುಣಿಕೆ - maddugunike (Flowers of India) ; ummatta (Wealth of India) |
| malayalam | ummatta |
| manipuri | ꯁꯒꯣꯜ ꯍꯤꯗꯥꯛ - sagol hidak (Flowers of India) |
| Indonésie | kucubung leutik (sundanais), jarak pendek, kacubung wulung (javanais) (PROSEA) |
| Thaïlande | lanphong khao (PROSEA) |
- Voir les noms de la Flore populaire d'Eugène Rolland
Classification
Datura stramonium L. (1753)
Cultivars
Histoire
Usages
- Voir les Plantes médicinales de Cazin (1868)
En fumigation, cette espèce s'emploie contre les maladies des organes génitaux féminins (BOUQUET, 1921 ; GATTEFOSSÉ, 1921).
FOLEY (1939) a signalé pour Datura stramonium la même propriété toxique que pour Datura metel.
CHOPRA et al. (1960) s'attachent à présenter les études chimiques et cliniques effectuées sur cette espèce et signalent qu'en culture, on coupe la totalité de la plante quand les fruits sont déjà à maturité. Après séchage à l'ombre, les capsules s'ouvrent et l'on récolte les graines ; les feuilles sont séchées à part. Le datura (PARIS et MOYSE, 1971) est un peu moins employé que la belladone, mais administré sous forme de poudre, teinture ou cigarette, il est cependant utilisé comme antispasmodique, antiasthmatique et antiparkinsonien, alors qu'en usage externe, les feuilles servent dans des préparations analgésiques.
L'espèce est toxique, révèlent LEMORDANT et al. (1977) qui rapportent également sa vertu parasympatholytique et ses dénominations en Tunisie (ar. = jaouz mtil).
Cultivated frequently in Europe and in some other parts of the world. In the second half of the 16th cent. D. stramonium reached Spain, from there it was brought into the rest of the European lands. Run wild in Europe since the end of the 17th cent. Used by Algonquins and other Amerindians as an inebriating medicine. Leaf blades gathered at flowering time are officinal (Folia Stramonii), in some lands also the seeds (Semen Stramonii). All plant parts are rich in tropane alkaloids. Important commercial source of tropane alkaloids.
Références
- TRAMIL, Pharmacopée végétale caribéenne, éd. scient. L. Germosén-Robineau. 2014. 3e éd. Santo Domingo, Canopé de Guadeloupe. 420 p. Voir sur Pl@ntUse
Liens
- BHL
- FAO Ecocrop
- Flora of China
- Grieve's herbal
- GRIN
- IPNI
- Mansfeld
- Moerman, Native American Ethnobotany
- NewCrop Purdue
- Plant List
- Plants for a future
- PROSEA sur Pl@ntUse
- PROTA sur Pl@ntUse
- Sierra de Baza (Espagne)
- TAXREF
- Tela Botanica
- Useful Tropical Plants Database
- Wikipédia
- Wikiphyto
- Wikwio - Adventices de l'Ouest de l'Océan Indien