Cynometra madagascariensis (PROTA)
Introduction |
Cynometra madagascariensis Baill.
- Protologue: Bull. Mens. Soc. Linn. Paris 1: 375 (1883).
- Family: Caesalpiniaceae (Leguminosae - Caesalpinioideae)
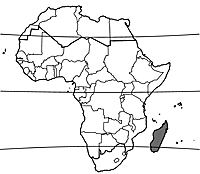
Origin and geographic distribution
Cynometra madagascariensis is endemic to eastern Madagascar, where it occurs from Sambava south to Taolañaro.
Uses
The wood, known as ‘mampay’ together with the wood of several other Cynometra spp. from Madagascar, is used for posts and planks in house construction.
Properties
Ethanolic leaf extracts of Cynometra madagascariensis showed potent antiviral activity against herpes simplex.
Description
- Evergreen small to medium-sized tree up to 20(–30) m tall; bole up to 50(–100) cm in diameter; twigs short-hairy, with lenticels.
- Leaves arranged spirally, paripinnately compound with (5–)6–16 pairs of leaflets; stipules threadlike, 0.5–1 cm long, caducous; petiole 1–3 mm long, thick, wrinkled, rachis 1–10 cm long, grooved above, short-hairy; leaflets opposite, sessile, obliquely oblong to oblong-ovate, 0.5–2(–2.5) cm × 0.2–0.6(–0.8) cm, notched at apex, glabrous. Inflorescence an axillary raceme up to 1.5 cm long, short-hairy; bracts small.
- Flowers bisexual, nearly regular, whitish; pedicel 0.5–1 cm long; sepals 4(–5), 2–3 mm long, reflexed; petals 5, free, narrowly obovate, 3.5–5 mm long; stamens 10, free, c. 7 mm long; ovary superior, with short stipe, hairy, 1-celled, style 3–5 mm long.
- Fruit a slightly obliquely oblong-elliptic, flat pod 1–2 cm × 0.5–2 cm, with short stipe, warty, 1-seeded.
- Seed with thin seed coat.
Other botanical information
Cynometra madagascariensis has been subdivided into 3 subspecies, differing in number and size of the leaflets and length of the leaf rachis. Trees flower from August to December.
Cynometra comprises about 90 species and occurs in the tropical regions of the world. Approximately 25 species can be found in mainland tropical Africa and about 10 in Madagascar. Tropical Asia and tropical America have about 25 species each.
The wood of several other Cynometra spp. is used in Madagascar for similar purposes as that of Cynometra madagascariensis.
Cynometra abrahamii
Cynometra abrahamii Du Puy & R.Rabev. is a medium-sized tree up to 30 m tall with bole up to 50 cm in diameter, widespread in deciduous woodland and evergreen forest. Its wood is used for posts in house construction and as roof support.
Cynometra aurita
Cynometra aurita R.Vig. is a small to medium-sized tree up to 25 m tall with bole up to 100 cm in diameter, endemic to lowland north-eastern Madagascar. The hard wood is used for construction.
Cynometra commersoniana
Cynometra commersoniana (DC.) Baill. is a small tree up to 12 m tall with bole up to 30 cm in diameter, occurring in lowland evergreen forest in eastern Madagascar. The hard and resilient wood is used for construction and tool handles, and as firewood.
Cynometra dauphinensis
Cynometra dauphinensis Du Puy & R.Rabev. is a small tree up to 15 m tall with bole up to 30 cm in diameter, also occurring in lowland evergreen forest in eastern Madagascar. Its dark-coloured wood is used for poles and planks in house construction, for carpentry, and as firewood.
Cynometra sakalava
Cynometra sakalava Du Puy & R.Rabev. is a small to medium-sized tree up to 25 m tall with bole up to 40 cm in diameter, fairly widespread in deciduous forest in northern and western Madagascar. The hard wood is used for poles in house construction, for carpentry, and as firewood.
Ecology
Cynometra madagascariensis occurs in evergreen coastal forest and hill forest up to 600 m altitude, on sandy and laterite soils.
Genetic resources
Cynometra madagascariensis does not appear to be liable to genetic erosion at present because it is widespread in eastern Madagascar. However, with the ongoing fragmentation of evergreen forest, monitoring of populations is recommended.
Prospects
The wood of Cynometra madagascariensis and other Cynometra spp. will remain of some importance in Madagascar for local applications, especially in house building. Little is known about nearly all aspects, and research is needed to do recommendations for future applications of the wood and sustainable exploitation of the trees.
Major references
- du Puy, D.J., Labat, J.N., Rabevohitra, R., Villiers, J.-F., Bosser, J. & Moat, J., 2002. The Leguminosae of Madagascar. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Richmond, United Kingdom. 750 pp.
- Hudson, J.B., Lee, M.K. & Rasoanaivo, P., 2000. Antiviral activities in plants endemic to Madagascar. Pharmaceutical Biology 38(1): 36–39.
Other references
- Schatz, G.E., 2001. Generic tree flora of Madagascar. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Richmond, United Kingdom. 477 pp.
Author(s)
- R.H.M.J. Lemmens, PROTA Network Office Europe, Wageningen University, P.O. Box 341, 6700 AH Wageningen, Netherlands
Correct citation of this article
Lemmens, R.H.M.J., 2011. Cynometra madagascariensis Baill. [Internet] Record from PROTA4U. Lemmens, R.H.M.J., Louppe, D. & Oteng-Amoako, A.A. (Editors). PROTA (Plant Resources of Tropical Africa / Ressources végétales de l’Afrique tropicale), Wageningen, Netherlands.
Accessed 18 December 2024.
- See the Prota4U database.