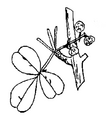
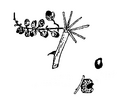
Zanthoxylum chalybeum (Maundu & Tengnäs, 2005)
| Zanthoxylum chalybeum (Maundu & Tengnäs, 2005) |
Zanthoxylum chalybeum (Fagara chalybea), Rutaceae, Indigenous
COMMON NAMES
- Boran: Gadda
- Chonyi: Mdungu
- Digo: Mdungu, Mudhungu
- Embu: Mugucua
- English: Knobwood
- Gabra: Gaddaa
- Giriama: Mudhungu, Mjafari
- Dchamus: Loisuki, Lousukui
- Kamba: Mukenea, Mukanu (Kitui)
- Kambe: Mdungu
- Kipsigis: Sagawaita
- Loo: Roko
- Maasai: Oloisuki, Oloisugi
- Marakwet: Songoiywa, Songorurwa
- Mbeere: Mugucwa, Mukenenga, Muruguci
- Meru: Mugucua
- Pokot: Songowo, Songoogh (plural)
- Samburu: Loisugi, Loisuki
- Sanya: Gadhayu korm
- Swahili: Mjafari
- Teso: Eusuk
- Tharaka: Muguuchwa
- Tugen: Kokian, Kokiin (plural)
- Turkana: Eusugu.
DESCRIPTION
- A spiny deciduous shrub or tree to 8 m, the crown rounded but open. The bole bas characteristic large, conical, woody knobs with sharp prickles at their tips. Branches with single dark-red recurved spines to 2 cm long.
- BARK: Pale grey, fissured or with ridges.
- LEAVES: Compound, a strong lemon smell if crushed, the leaf stalk with hooked prickles below, 6-9 pairs of shiny leaflets.
- FLOWERS: Yellow-green, in short heads below leaves on new branchlets. Male and female flowers on different trees.
- FRUIT: Red-brown-purple, like berries, open to release shiny black seeds.
ECOLOGY
Widespread in West Africa from Senegal, Nigeria and Cameroon to eastern Africa and south to Angola and Zambia. Found in most parts of Kenya in dry woodland, bushland or grassland, often on termite mounds and in rocky areas, on the coast and also in dry forest and closed thicket near the sea, 0-1,500 m. Agroclimatic Zone V.
USES
Firewood, charcoal, timber, fumiture, poles (construction), carvings, drink (dried leaves used as tea leaves), flavouring (stem pieces for soup), fragrance (crushed seed in a mix with oil), medicine (leaves, bark and roots), fodder (leaves and fruit), toothbrushes, veterinary medicine, seeds used as beads in traditional garments.
PROPAGATION
Seedlings, wildings, root suckers, root cuttings.
SEED
- About 30,000 seeds per kg; germination 70-80%.
- treatment: Not necessary.
- storage: Sow immediately after collection.
MANAGEMENT
Pruning, coppicing, pollarding.
REMARKS
The wood produces excellent charcoal. Before charcoal was introduced to Tharaka, the woody knobs on the bole were burned to produce an intense heat used for smelting metal. A related species, Z. holtzianum (Swahili: Mjafari), grows with this species all along the coast into Somalia and can grow on coral, 0-230 m. It is very similar but smaller, sometimes a climber, the leaf stalk without prickles, the small fruit scarlet and dotted with glands. It is used for carving and for medicine.
Crushed leaves smell of aniseed or betel nut. Zanthoxylum is a tropical and subtropical genus of both the Old and New Worlds, including Australia, and the species are well-known medicinal and timber plants. The fruits of some species are used as condiments, and chewing sticks from roots of some species are known to have antimicrobial activity and are useful against oral micro-organisms.
FURTHER READING
- http://www.worldagroforestrycentre.org/Sites/TreeDBS/AFf/AFf.htm
- Beentje, 1994
- ITDG and DRR, 1996
- Katende et al., 1995, 1999
- Kokwaro, 1993
- Maundu et al., 1999
- Mbuya et al., 1994
- Palgrave and Palgrave, 2002
- Ruffo et al., 2002
- Storrs, 1979.