Blyttia fruticulosa (PROTA)
Introduction |
| General importance | |
| Geographic coverage Africa | |
| Geographic coverage World | |
| Fruit | |
| Medicinal | |
| Forage / feed | |
| Food security | |
Blyttia fruticulosa (Decne.) D.V.Field
- Protologue: Kew Bull. 38(2): 216 (1983), as ‘fruticulosum’.
- Family: Asclepiadaceae (APG: Apocynaceae)
- Chromosome number: 2n = 22
Synonyms
- Cynanchum defoliascens K.Schum. (1897).
Origin and geographic distribution
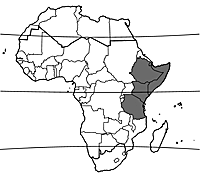
Blyttia fruticulosa occurs in Ethiopia, Djibouti, Somalia, Kenya and Tanzania and also in Saudi Arabia.
Uses
In Kenya, Turkana women drink an infusion of the aerial parts to treat painful menstruation. In Djibouti the Afar people eat the fresh fruits as a vegetable.
Goats, sheep, camels and donkeys browse the plant.
Description
Shrub up to 80 cm tall, with rather erect, straight branches; young branches grey-green, twining occasionally up to 2 m long, with clear juice. Leaves opposite, simple, glabrous; stipules absent; petiole short; blade linear or narrowly oblong to elliptical, 7–30 mm × 1–5 mm, base rounded, apex rounded to acute, margin entire. Inflorescence an axillary, slender, few-flowered umbel up to c. 2 cm long; peduncle 3–7(–18) mm long. Flowers bisexual, regular, 5-merous, small, whitish; pedicel 1–3 mm long; corolla white or greenish, with ovate lobes, 1–2.5 mm long, corona lobes c. 0.7 mm long; stamens inserted on the corolla, anthers connivent around the conical stigmatic head, forming a ‘gynostegium’, with apical appendages. Fruit a single, pendent follicle, thin-walled, narrowly cylindrical, 2.5–5 cm long, with attenuate beak. Seeds smooth, winged, bearing a coma of long silky hairs at one end.
Other botanical information
Blyttia comprises 2 species, Blyttia fruticulosa and Blyttia spiralis (Forssk.) D.V.Field & J.R.I.Wood, which occurs in East Africa as well.
Ecology
Blyttia fruticulosa occurs in open Acacia-Commiphora bushland on sand, silty or rocky soils, from sea-level up to 1500 m altitude.
Genetic resources
There are no signs that Blyttia fruticulosa is threatened by genetic erosion.
Prospects
Blyttia fruticulosa will remain of local importance, unless chemical and pharmacological research reveals interesting properties.
Major references
- Gilbert, M., Goyder, D., Lavranos, J., Liede-Schumann, S., Thulin, M. & Venter, J., 2006. Apocynaceae (incl. Asclepiadaceae). In: Thulin, M. (Editor). Flora of Somalia. Volume 3. Angiospermae (cont.). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Richmond, United Kingdom. p. 117–197.
- Kokwaro, J.O., 1993. Medicinal plants of East Africa. 2nd Edition. Kenya Literature Bureau, Nairobi, Kenya. 401 pp.
Other references
- Heine, B. & Heine, I., 1988. Plant concepts and plant use; an ethnobotanical survey of the semi-arid and arid lands of East Africa. Part 3. Rendille plants (Kenya). Cologne Development Studies 8. Breitenbach, Saarbrücken, Germany. 120 pp.
- Kiambi, D., 1999. Assessment of the status of agrobiodiversity in Djibouti: a contribution to the National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan. Draft report. IPGRI, Nairobi, Kenya. 61 pp.
Author(s)
- G.H. Schmelzer, PROTA Network Office Europe, Wageningen University, P.O. Box 341, 6700 AH Wageningen, Netherlands
Correct citation of this article
Schmelzer, G.H., 2010. Blyttia fruticulosa (Decne.) D.V.Field. In: Schmelzer, G.H. & Gurib-Fakim, A. (Editors). PROTA (Plant Resources of Tropical Africa / Ressources végétales de l’Afrique tropicale), Wageningen, Netherlands. Accessed 3 April 2025.
- See the Prota4U database.