Annona senegalensis (Bekele-Tesemma, 2007)
| Annona senegalensis (Bekele-Tesemma, 2007) |
Annona senegalensis (A. chrysophylla) Annonaceae Indigenous
Common names
- English: Wild custard apple
- Afargna: Gishita
- Amargna: Giishta, Yebere lib
- Oromugna: Komate
- Wolaytgna: Eta
Ecology
The species is widespread in tropical Africa, from Senegal to South Africa and Madagascar in semi-arid to subhumid regions. In Ethiopia, it is found in Combretum woodland and wooded grassland in the Moist and Wet Kolla agroclimatic zones of Wolega, Gojam, Ilubabor, Kefa, Gamo Gofa and Bale regions, 400–1,600 m.
Uses
Firewood, timber, poles, tool handles, food (fruit), medicine (roots, gum, fruit), fodder (leaves, fruit), ornamental, windbreak, fibre (bark), yellow-brown dye (bark).
Description
A shrub-like tree, 2–10 m.
- BARK: grey and smooth, thick and folded when old, young stems hairy and orange‑red.
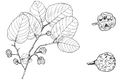
- LEAVES: Broadly oval, 15 x 10 cm, blue‑green, hairy below, fragrant when crushed, on a short thick stalk.
- FLOWERS: Solitary or in bunches of 2–4, small flowers hanging down below twigs, yellowish with petals and sepals in threes; petals thick and hard, many stamens.
- FRUIT: Rounded 2–7 cm smooth with divisions. Pick green and unripe. When orange‑yellow and smelling like pineapple the sweet pulp is edible. Seeds numerous and orange-brown.
Propagation
Seedlings (sow seeds in pots), wildings, root suckers from exposed or injured roots.
Seed
2,500–4,000 seed per kg.
- Treatment: Not necessary.
- Storage: Seeds susceptible to insect damage and lose viability within 6 months. Add ash to reduce insect damage.
Management
Prune to stimulate branching at comfortable height.
Remarks
Roots used to treat colds; fruit against diarrhoea, dysentery and vomiting. Gum from the bark used to seal cuts and wounds, and even to plug leaking pots.