Aloe vera
From PlantUse English
Revision as of 18:02, 21 February 2021 by Eléa HEBERLE (Talk | contribs)
Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f.
| Order | Asparagales |
|---|---|
| Family | Asphodelaceae |
| Genus | Aloe |
2n = 14
Origin : North-East Africa
cultivated
| English | "Aloe vera" |
|---|---|
| French | "aloès" |
To edit this page, please copy the French version and translate it. If it contains no data, the first tasks are to check all the links, to clarify nomenclature and to upload photos from Wikimedia Commons
Uses summary
- medicinal :
- exudate : laxative, purgative, vermifuge
- gel : skin affections
- gel used in the manufacture of jellies, drinks and ice cream
- gel: food supplement
- leaves and seeds are consumed as vegetables
- ornemental
Contents
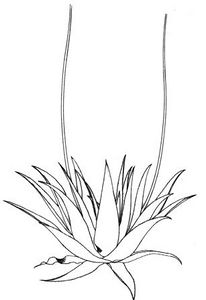
Description
- stemless or short-stemmed plant, stoloniferous
- fleshy lanceolate leaves, 30 to 60 cm long, ending in a fine point, prickly toothed
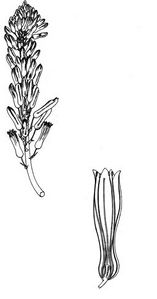
- inflorescence on a stipe up to 1.2 m, with lanceolate or ovate bracts, pointed
- yellow flowers 2.5 cm long in dense clusters of 10 to 30 cm
- fruit: dehiscent capsule
- black seeds
Popular names
| english | aloe vera, Barbados aloe, coastal aloe, Curaçao aloe, Indian aloe, medicinal aloe, Mediterranean aloe, true aloe, West Indian aloe |
| french | aloès, aloès vulgaire, aloe vera |
| guyanese creole | aloé [lalwès, lalowès] (Pharma. Guyane) |
| palikur | punamna arib (Pharma. Guyane) |
| portuguese | aloés, aloé vera, aloés de Barbados, caraguatá, erva babosa, babosa, azebre vegetal |
Classification
Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f. (1768) (between March 1st and April 6th)
basionym :
- Aloe perfoliata var. vera L. (1753)
synonyms :
- Aloe barbadensis Mill. (1768) (April 16th, after Burman)
- Aloe indica Royle (1840), nom. nud.
Cultivars
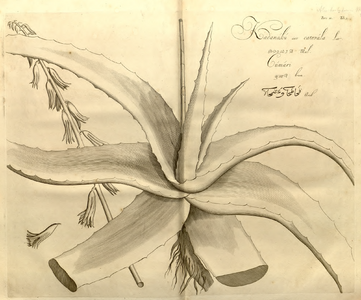
History
aloê folio 15r, Dioscoride, Codex Vindobonensis Med. Gr. I
kadanaku vol. 11 pl. 3 Rheede 1692, Hortus malabaricus
Uses
References
- Bekele-Tesemma, Azene, 2007. Useful trees and shrubs for Ethiopia. Identification, propagation and management for 17 agroclimatic zones. Nairobi, ICRAF - RELMA. 550 p. (Technical Manual 6). Voir l'article
- Chauvet, Michel, 2018. Encyclopédie des plantes alimentaires. Paris, Belin. 880 p. (p. 82)
- Grenand, Pierre ; Moretti, Christian ; Jacquemin, Henri & Prévost, Marie-Françoise, 2004. Pharmacopées traditionnelles en Guyane. Créoles, Wayãpi, Palikur. 2e édition revue et complétée. Paris, IRD. 816 p. (1ère éd.: 1987). Voir sur Pl@ntUse.
- TRAMIL, Pharmacopée végétale caribéenne, éd. scient. L. Germosén-Robineau. 2014. 3e éd. Santo Domingo, Canopé de Guadeloupe. 420 p. Voir sur Pl@ntUse